Have you ever wondered what actually happens when you visit a dermatologist for acne? Well, wonder no more! In this article, we will take you through the journey of a typical dermatologist appointment for acne, from the moment you step into the clinic to the various treatments and advice you might receive. Join us as we explore the world of dermatology and discover how these skincare experts can help you achieve clear and healthy skin.
Initial Consultation
Setting Up an Appointment
When you decide to visit a dermatologist for your acne concerns, the first step is to set up an appointment. This can usually be done by contacting the dermatologist’s office directly, either by phone or through their website. The appointment desk will guide you through the process, asking for your basic details and scheduling a convenient date and time for your visit. It is essential to be proactive in seeking an appointment, as dermatologists often have busy schedules.
Medical History Assessment
During your initial consultation for acne, your dermatologist will begin by assessing your medical history. They will ask you questions about your past and current medical conditions, previous treatments for acne, and any medications you may be taking. It is crucial to provide as much detail as possible to help the dermatologist understand your acne better and make an accurate diagnosis. Being open and honest about your medical history will enable your dermatologist to tailor a treatment plan specifically for you.
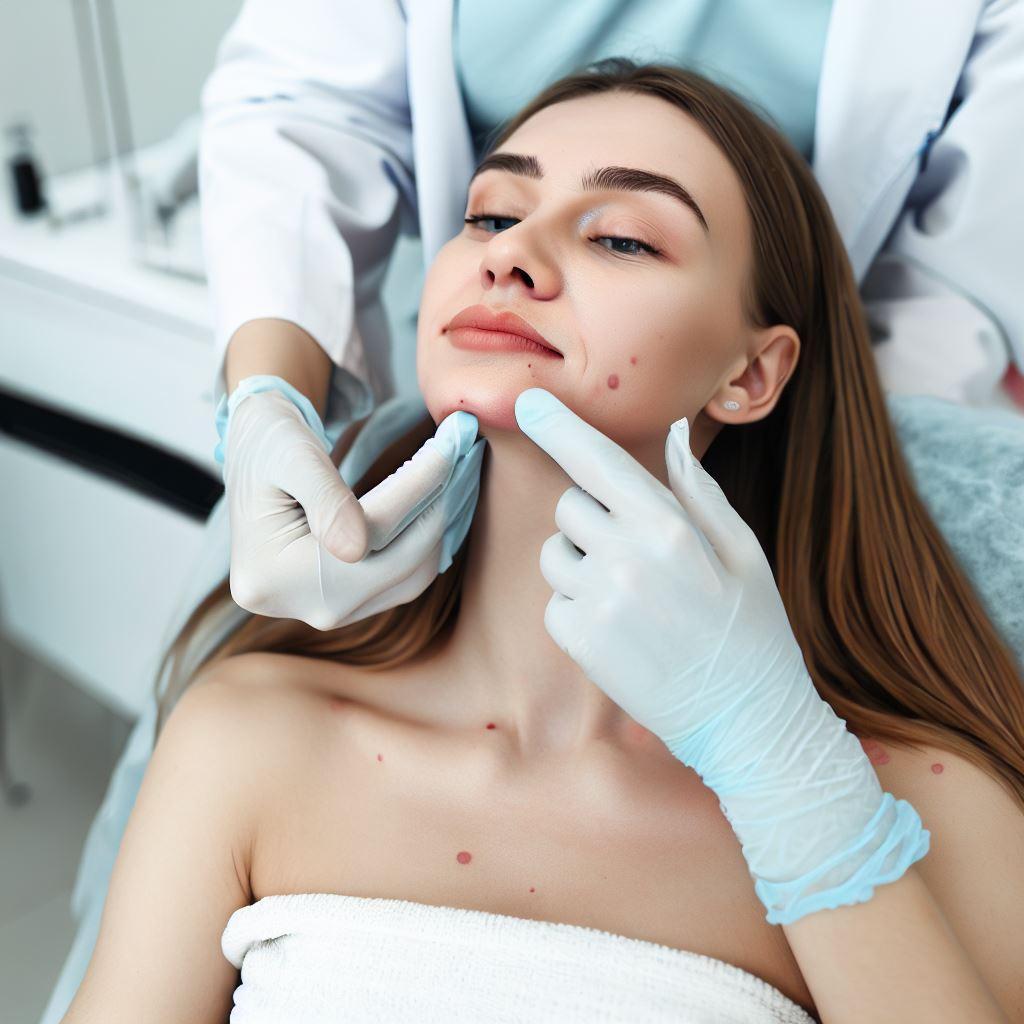
Visual Examination of the Skin
Once your medical history is assessed, your dermatologist will proceed with a thorough visual examination of your skin. They will closely inspect the areas affected by acne, looking for specific types of lesions, such as blackheads, whiteheads, pimples, or cysts. By examining your skin, the dermatologist can determine the severity of your acne and identify any potential complications or comorbidities. You should be prepared to have your skin examined, as it is an essential step in the diagnostic process.
Discussion of Acne Symptoms
During the consultation, your dermatologist will also engage in a detailed discussion about your acne symptoms. They will ask you questions about the duration of your acne, the frequency of breakouts, and any triggers you may have noticed. It is vital to provide accurate information and not hesitate to share any concerns or symptoms you may have experienced. This open discussion will aid your dermatologist in developing an effective treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
Possible Triggers and Contributing Factors
In addition to discussing your acne symptoms, your dermatologist will inquire about possible triggers and contributing factors that may be exacerbating your condition. These can range from hormonal imbalances and stress to certain skincare products and dietary habits. By identifying these triggers, your dermatologist can provide you with guidance on lifestyle modifications that may help improve your acne. Understanding the factors that influence your acne can be instrumental in managing the condition effectively.
Diagnosis and Severity Assessment
Different Types of Acne
Acne is not a one-size-fits-all condition. There are various types of acne that can affect individuals differently. Your dermatologist will explain the different types of acne, such as blackheads (open comedones), whiteheads (closed comedones), papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts. By understanding the specific type of acne you have, your dermatologist can determine the most appropriate treatment options for you.
Determining Acne Severity
As part of the diagnosis process, your dermatologist will also assess the severity of your acne. Acne severity is generally classified as mild, moderate, or severe, and this classification helps guide the treatment approach. Your dermatologist will evaluate factors such as the number of lesions, degree of inflammation, and presence of scarring to determine the severity level. This assessment will assist in formulating an individualized treatment plan that effectively addresses your acne concerns.
Identification of Comorbidities
In some cases, acne may be associated with underlying comorbidities. These coexisting conditions can range from hormonal disorders, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), to other skin conditions like rosacea. Your dermatologist will carefully assess your medical history, examine your skin, and ask relevant questions to identify any potential comorbidities that may be contributing to your acne. Understanding these associations is essential for accurate diagnosis and developing a comprehensive treatment plan.
Possible Skin Condition Tests
Depending on your specific case and the dermatologist’s initial assessment, additional tests may be required to confirm a diagnosis or rule out other skin conditions. These tests can include skin swabs, biopsies, or patch tests. Skin swabs are helpful in identifying any bacterial or fungal infections that may be present. Biopsies, although less common, may be performed if there is suspicion of a different type of skin condition. Patch tests are conducted to determine if certain substances or allergens are triggering your acne. Your dermatologist will discuss the necessity of these tests with you and explain the procedure if they are required.
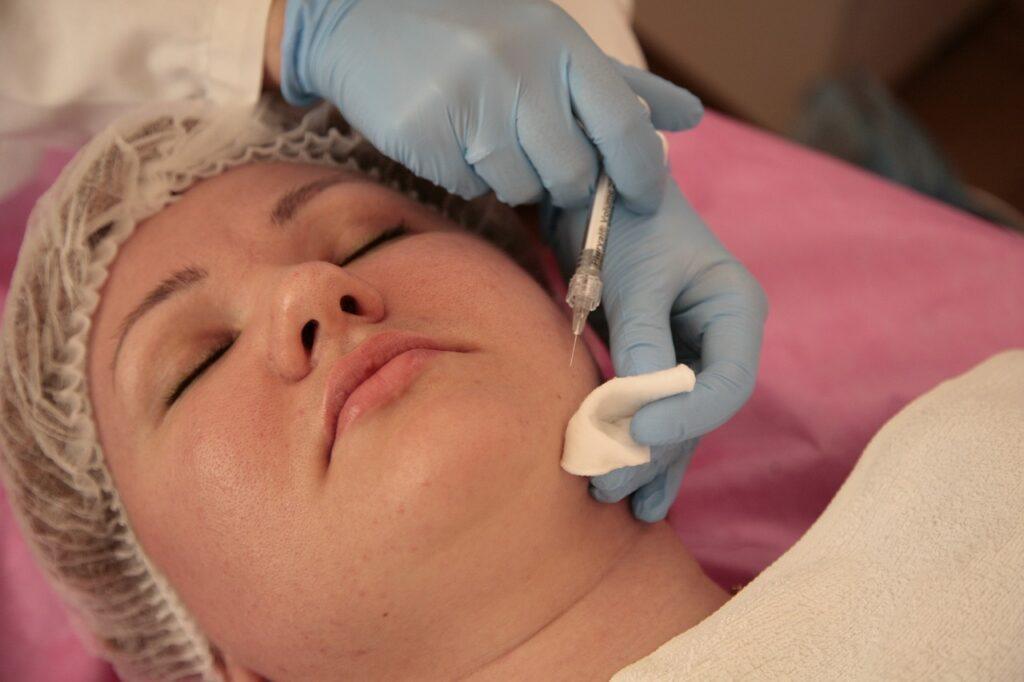
Treatment Options
Topical Medications
Topical medications are often the first line of treatment for acne. These medications can come in the form of creams, gels, lotions, or solutions that are applied directly to the affected areas of the skin. Common topical treatments for acne include benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, retinoids, and antibiotics. Your dermatologist will prescribe the most suitable topical medication for your specific type and severity of acne, taking into consideration your skin sensitivity and any allergies you may have.
Oral Medications
In cases of moderate to severe acne or when topical treatments have not provided sufficient improvement, oral medications may be recommended. Oral antibiotics, such as tetracycline or erythromycin, can help reduce inflammation and control bacterial growth. For females with hormonal acne, combined oral contraceptives (birth control pills) or anti-androgen medications may be prescribed to regulate hormone levels. Oral isotretinoin, a potent medication, is reserved for severe, nodular acne when other treatments have not been successful. Your dermatologist will carefully assess your specific situation to determine the appropriate oral medication for you.
Combination Therapies
Combination therapy involves using multiple treatment approaches simultaneously to maximize effectiveness. This approach may include combining oral and topical medications, such as using oral antibiotics alongside a topical retinoid. Combination therapies can provide more comprehensive control of acne and prevent the development of antibiotic resistance. Your dermatologist will design a combination treatment plan tailored to your individual needs, aiming to target different aspects of acne formation.
Physical Treatments
In certain cases, physical treatments may be recommended to address specific acne lesions or improve overall skin appearance. Physical treatments can include procedures like chemical peels, microdermabrasion, and dermabrasion. These treatments help exfoliate the skin, unclog pores, and promote the growth of healthier skin cells. Your dermatologist will assess your skin condition and determine if any physical treatments would be beneficial for you. They will carefully explain the procedure, expected outcomes, and any potential side effects or downtime.
Acne Surgery
Acne surgery is a specialized procedure performed by dermatologists to remove deep acne cysts or nodules. This procedure involves making a small incision, draining the lesion, and sometimes removing the sack to prevent recurrence. Acne surgery is typically recommended for severe, cystic acne that does not respond well to other treatments. Your dermatologist will discuss the details of the procedure, including any necessary precautions or post-operative care instructions.
Extraction Procedures
Extraction procedures, also known as acne extractions or acne facials, are a manual method of removing certain types of acne lesions, such as blackheads or whiteheads. This procedure involves using sterile instruments to gently extract the contents of the blocked pores. While extraction procedures can provide immediate relief by removing visible acne lesions, they are best performed by a dermatologist or trained skincare professional to minimize the risk of infection or scarring. Your dermatologist will determine if extraction procedures are suitable for your specific case.
Light and Laser Therapies
Light and laser therapies have become popular treatment options for acne. These therapies target specific factors involved in acne formation, such as bacteria, inflammation, and sebum production. Light and laser treatments can help reduce acne lesions, minimize redness and inflammation, and improve overall skin texture. Common light and laser therapies include blue light therapy, photodynamic therapy, and laser resurfacing. Your dermatologist will discuss the available light and laser treatment options and recommend the most appropriate one based on your acne severity and skin type.

Skincare Advice and Education
Importance of Cleansing Routine
Proper skincare is crucial for managing acne and preventing future flare-ups. Your dermatologist will provide guidance on establishing an effective cleansing routine. This routine typically involves cleansing your face twice daily with a mild, non-comedogenic cleanser to remove excess oil, dirt, and dead skin cells. It is important to avoid harsh scrubbing or using abrasive cleansers, as this can irritate the skin and worsen acne. Your dermatologist may recommend specific cleansers suitable for your skin type and acne condition.
Use of Non-Comedogenic Products
Non-comedogenic products are skincare or cosmetic products formulated to avoid clogging the pores. Using non-comedogenic products can prevent the formation of new acne lesions and minimize the risk of breakouts. Your dermatologist will emphasize the importance of choosing non-comedogenic cleansers, moisturizers, sunscreens, and makeup. They may recommend specific brands or ingredients that are suitable for your skin type.